Tutorial despre cum sa desenezi un cub 3D cu Open GL, sa-l rotesti si sa pui 6 imagini, cate una pe fiecare fata a sa.
Deschidem Eclipse si cream un proiect nou (vezi aici cum) pe care il denumim FotoCub.
Punem 6 imagini (pe care vrem sa le punem pe fetele cubului) din pc (cu copy-paste) in res -> drawable-hdpi.
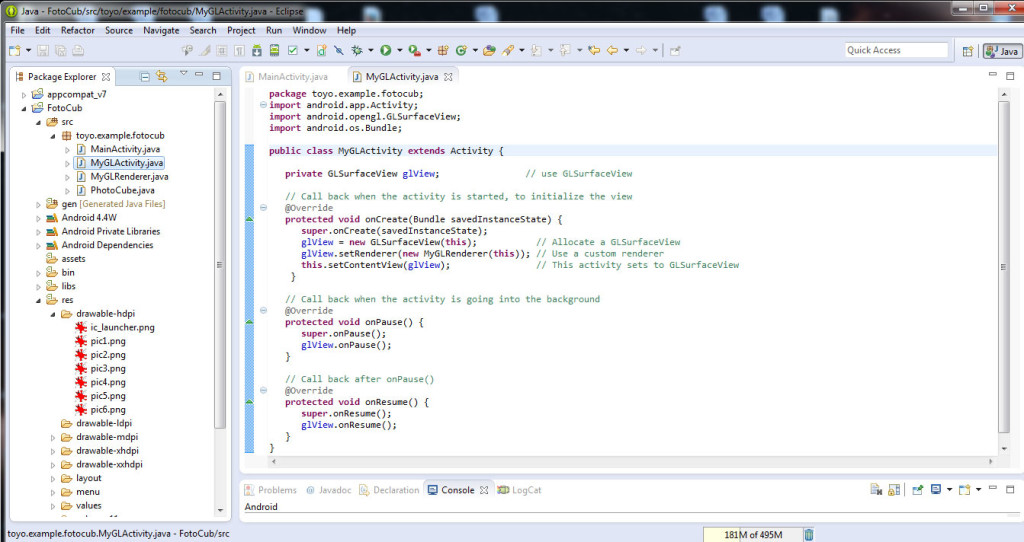
Dam click dreapta pe folderul FotoCub al proiectului nostru si selectam New -> Class. Se deschide o fereastra in care se completeaza numele noii clase: MyGLActivity. In acest fisier scriem codul:
package toyo.example.fotocub;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.opengl.GLSurfaceView;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MyGLActivity extends Activity {
private GLSurfaceView glView; // use GLSurfaceView
// Call back when the activity is started, to initialize the view
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
glView = new GLSurfaceView(this); // Allocate a GLSurfaceView
glView.setRenderer(new MyGLRenderer(this)); // Use a custom renderer
this.setContentView(glView); // This activity sets to GLSurfaceView
}
// Call back when the activity is going into the background
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
glView.onPause();
}
// Call back after onPause()
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
glView.onResume();
}
}
Cream o noua clasa, ca si mai sus, pe care o denumim MyGLRenderer si in care scriem urmatorul cod:
package toyo.example.fotocub;
import javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGLConfig;
import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10;
import android.content.Context;
import android.opengl.GLSurfaceView;
import android.opengl.GLU;
public class MyGLRenderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer {
private PhotoCube cube; // (NEW)
private static float angleCube = 0; // rotational angle in degree for cube
private static float speedCube = 0.5f; // rotational speed for cube
// Constructor
public MyGLRenderer(Context context) {
cube = new PhotoCube(context); // (NEW)
}
// Call back when the surface is first created or re-created.
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl, EGLConfig config) {
gl.glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); // Set color's clear-value to black
gl.glClearDepthf(1.0f); // Set depth's clear-value to farthest
gl.glEnable(GL10.GL_DEPTH_TEST); // Enables depth-buffer for hidden surface removal
gl.glDepthFunc(GL10.GL_LEQUAL); // The type of depth testing to do
gl.glHint(GL10.GL_PERSPECTIVE_CORRECTION_HINT, GL10.GL_NICEST); // nice perspective view
gl.glShadeModel(GL10.GL_SMOOTH); // Enable smooth shading of color
gl.glDisable(GL10.GL_DITHER); // Disable dithering for better performance
// Setup Texture, each time the surface is created (NEW)
cube.loadTexture(gl); // Load images into textures (NEW)
gl.glEnable(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D); // Enable texture (NEW)
}
// Call back after onSurfaceCreated() or whenever the window's size changes
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) {
if (height == 0) height = 1; // To prevent divide by zero
float aspect = (float)width / height;
// Set the viewport (display area) to cover the entire window
gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
// Setup perspective projection, with aspect ratio matches viewport
gl.glMatrixMode(GL10.GL_PROJECTION); // Select projection matrix
gl.glLoadIdentity(); // Reset projection matrix
// Use perspective projection
GLU.gluPerspective(gl, 45, aspect, 0.1f, 100.f);
gl.glMatrixMode(GL10.GL_MODELVIEW); // Select model-view matrix
gl.glLoadIdentity(); // Reset
// You OpenGL|ES display re-sizing code here
// ......
}
// Call back to draw the current frame.
@Override
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) {
// Clear color and depth buffers
gl.glClear(GL10.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL10.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// ----- Render the Cube -----
gl.glLoadIdentity(); // Reset the model-view matrix
gl.glTranslatef(0.0f, 0.0f, -6.0f); // Translate into the screen
gl.glRotatef(angleCube, 0.15f, 1.0f, 0.3f); // Rotate
cube.draw(gl);
// Update the rotational angle after each refresh.
angleCube += speedCube;
}
}
Cream o noua clasa, ca si mai sus, pe care o denumim PhotoCube si in care scriem urmatorul cod:
package toyo.example.fotocub;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.nio.FloatBuffer;
import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.opengl.GLUtils;
/*
* A photo cube with 6 pictures (textures) on its 6 faces.
*/
public class PhotoCube {
private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer; // Vertex Buffer
private FloatBuffer texBuffer; // Texture Coords Buffer
private int numFaces = 6;
private int[] imageFileIDs = { // Image file IDs
R.drawable.pic1,
R.drawable.pic2,
R.drawable.pic3,
R.drawable.pic4,
R.drawable.pic5,
R.drawable.pic6
};
private int[] textureIDs = new int[numFaces];
private Bitmap[] bitmap = new Bitmap[numFaces];
private float cubeHalfSize = 1.2f;
// Constructor - Set up the vertex buffer
public PhotoCube(Context context) {
// Allocate vertex buffer. An float has 4 bytes
ByteBuffer vbb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(12 * 4 * numFaces);
vbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
vertexBuffer = vbb.asFloatBuffer();
// Read images. Find the aspect ratio and adjust the vertices accordingly.
for (int face = 0; face < numFaces; face++) {
bitmap[face] = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(
context.getResources().openRawResource(imageFileIDs[face]));
int imgWidth = bitmap[face].getWidth();
int imgHeight = bitmap[face].getHeight();
float faceWidth = 2.0f;
float faceHeight = 2.0f;
// Adjust for aspect ratio
if (imgWidth > imgHeight) {
faceHeight = faceHeight * imgHeight / imgWidth;
} else {
faceWidth = faceWidth * imgWidth / imgHeight;
}
float faceLeft = -faceWidth / 2;
float faceRight = -faceLeft;
float faceTop = faceHeight / 2;
float faceBottom = -faceTop;
// Define the vertices for this face
float[] vertices = {
faceLeft, faceBottom, 0.0f, // 0. left-bottom-front
faceRight, faceBottom, 0.0f, // 1. right-bottom-front
faceLeft, faceTop, 0.0f, // 2. left-top-front
faceRight, faceTop, 0.0f, // 3. right-top-front
};
vertexBuffer.put(vertices); // Populate
}
vertexBuffer.position(0); // Rewind
// Allocate texture buffer. An float has 4 bytes. Repeat for 6 faces.
float[] texCoords = {
0.0f, 1.0f, // A. left-bottom
1.0f, 1.0f, // B. right-bottom
0.0f, 0.0f, // C. left-top
1.0f, 0.0f // D. right-top
};
ByteBuffer tbb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(texCoords.length * 4 * numFaces);
tbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
texBuffer = tbb.asFloatBuffer();
for (int face = 0; face < numFaces; face++) {
texBuffer.put(texCoords);
}
texBuffer.position(0); // Rewind
}
// Render the shape
public void draw(GL10 gl) {
gl.glFrontFace(GL10.GL_CCW);
gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);
gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_COORD_ARRAY);
gl.glVertexPointer(3, GL10.GL_FLOAT, 0, vertexBuffer);
gl.glTexCoordPointer(2, GL10.GL_FLOAT, 0, texBuffer);
// front
gl.glPushMatrix();
gl.glTranslatef(0f, 0f, cubeHalfSize);
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureIDs[0]);
gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 0, 4);
gl.glPopMatrix();
// left
gl.glPushMatrix();
gl.glRotatef(270.0f, 0f, 1f, 0f);
gl.glTranslatef(0f, 0f, cubeHalfSize);
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureIDs[1]);
gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 4, 4);
gl.glPopMatrix();
// back
gl.glPushMatrix();
gl.glRotatef(180.0f, 0f, 1f, 0f);
gl.glTranslatef(0f, 0f, cubeHalfSize);
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureIDs[2]);
gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 8, 4);
gl.glPopMatrix();
// right
gl.glPushMatrix();
gl.glRotatef(90.0f, 0f, 1f, 0f);
gl.glTranslatef(0f, 0f, cubeHalfSize);
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureIDs[3]);
gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 12, 4);
gl.glPopMatrix();
// top
gl.glPushMatrix();
gl.glRotatef(270.0f, 1f, 0f, 0f);
gl.glTranslatef(0f, 0f, cubeHalfSize);
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureIDs[4]);
gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 16, 4);
gl.glPopMatrix();
// bottom
gl.glPushMatrix();
gl.glRotatef(90.0f, 1f, 0f, 0f);
gl.glTranslatef(0f, 0f, cubeHalfSize);
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureIDs[5]);
gl.glDrawArrays(GL10.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 20, 4);
gl.glPopMatrix();
gl.glDisableClientState(GL10.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY);
gl.glDisableClientState(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_COORD_ARRAY);
}
// Load images into 6 GL textures
public void loadTexture(GL10 gl) {
gl.glGenTextures(6, textureIDs, 0); // Generate texture-ID array for 6 IDs
// Generate OpenGL texture images
for (int face = 0; face < numFaces; face++) {
gl.glBindTexture(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureIDs[face]);
gl.glTexParameterf(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL10.GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL10.GL_NEAREST);
gl.glTexParameterf(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL10.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL10.GL_LINEAR);
// Build Texture from loaded bitmap for the currently-bind texture ID
GLUtils.texImage2D(GL10.GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, bitmap[face], 0);
bitmap[face].recycle();
}
}
}
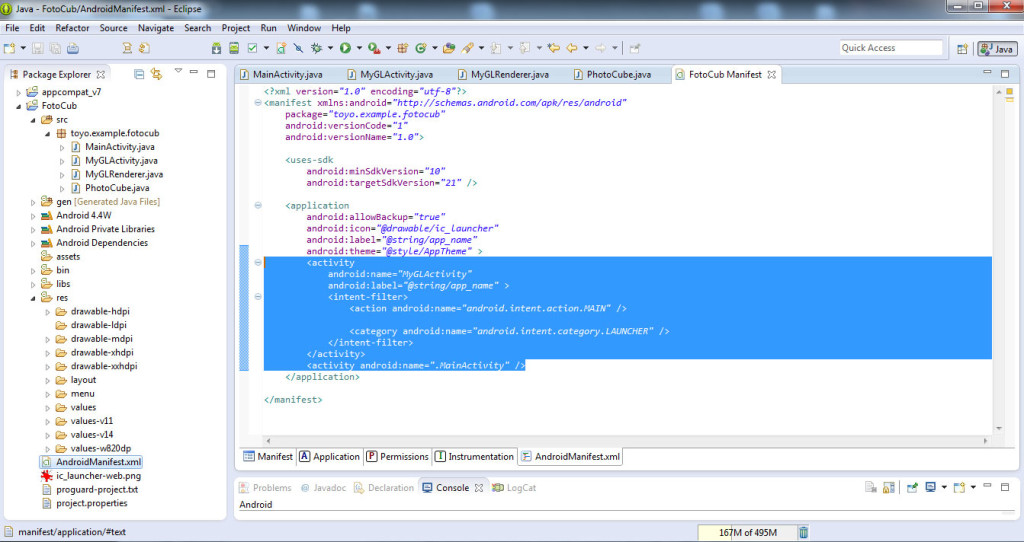
In fisierul AndroidManifest.xml al proiectului modificam codul:
<activity android:name="MyGLActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name=".MainActivity" />
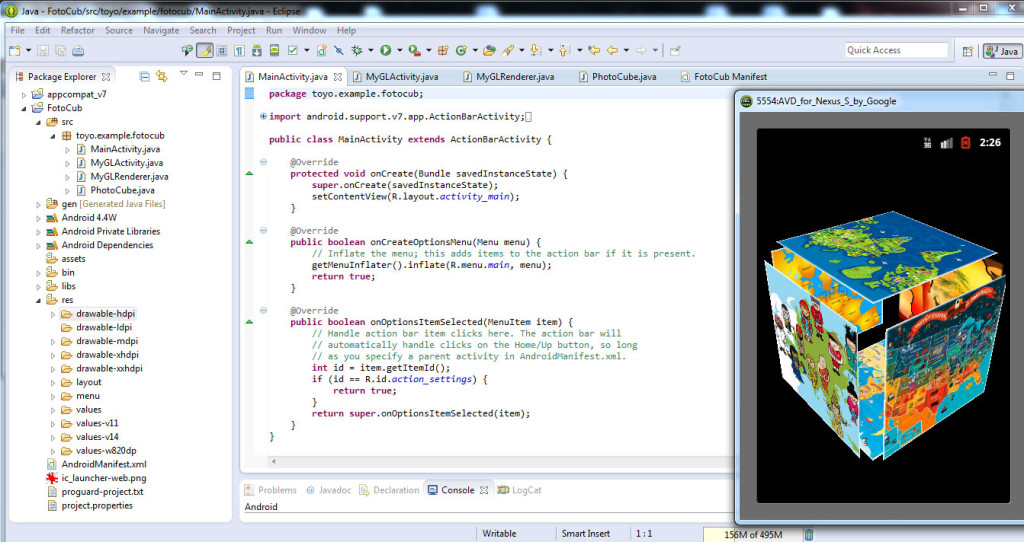
Rulam aplicatia si vedem rezultatul final: un cub 3D care se roteste si care are pe fiecare fata a sa, cate una din pozele pe care le-am inclus in proiect.
Vezi aici cum poti sa-ti salvezi aplicatia in vederea rularii ei pe telefonul mobil.
Proiectul (cu toate fisierele) realizat se poate downloada de AICI.
Aplicatia pentru telefonul mobil se poate downloada de AICI.
Dupa ce se downloadeaza, se copiaza in telefonul mobil si se instaleaza.
Vezi aici exemplu de aplicatie cu cub 3D cu 6 poze, animat.
Urmareste tutorialul video despre cum sa creezi un cub cu 6 fotografii care se roteste in Android: